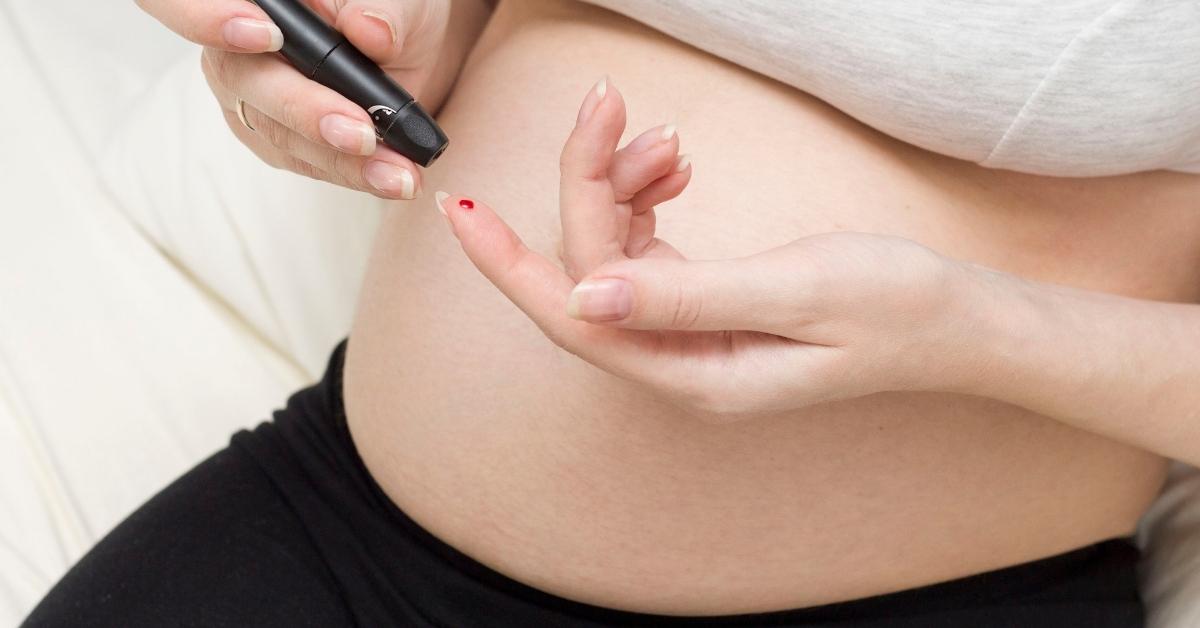
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that appears for the first time during pregnancy in pregnant women who have never had the disease before. In some women, gestational diabetes may affect them in more than one pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually appears in mid-pregnancy. Doctors usually perform tests between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes can often be controlled with healthy eating and regular exercise, but sometimes the mother will also need insulin.
Problems of gestational diabetes in pregnancy
Blood sugar that is not well controlled in gestational diabetes can lead to problems in the mother and her baby:
A baby that is too big
Diabetes that is not well controlled causes a rise in the baby’s blood sugar. The baby is “overfed” and grows too large. In addition to causing discomfort for the mother in the last months of pregnancy, an extra large baby can cause problems during delivery for both her and the baby.
Cesarean section
A woman with poorly controlled diabetes is more likely to require a cesarean section. When the baby is delivered by cesarean section, it takes longer for the mother to recover from the delivery.
High blood pressure (preeclampsia)
High blood pressure can cause harm to both the mother and her unborn baby. It can cause premature delivery of the baby and also seizures or strokes in the woman during labor and delivery. Women with diabetes have high blood pressure more often than women without diabetes.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
People with diabetes who take insulin or other diabetes medications may have low blood sugar. Low blood sugar can be serious and even deadly if not treated quickly.
Tips for women with gestational diabetes
Eat healthy foods
Eat healthy foods included in a meal plan for people with diabetes.
Exercise regularly
Exercise is another way to control blood sugar. It helps level out your food intake. You can exercise regularly during and after pregnancy. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity at least five days a week.
Check your blood sugar frequently
Because pregnancy causes changes in the body’s energy needs, blood sugar levels can change very quickly.
Take insulin, if you need it
Sometimes women with gestational diabetes need to take insulin. If your doctor prescribes insulin, use it as directed to control your blood sugar.
Proper management of diabetes during pregnancy is critical to prevent maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality.