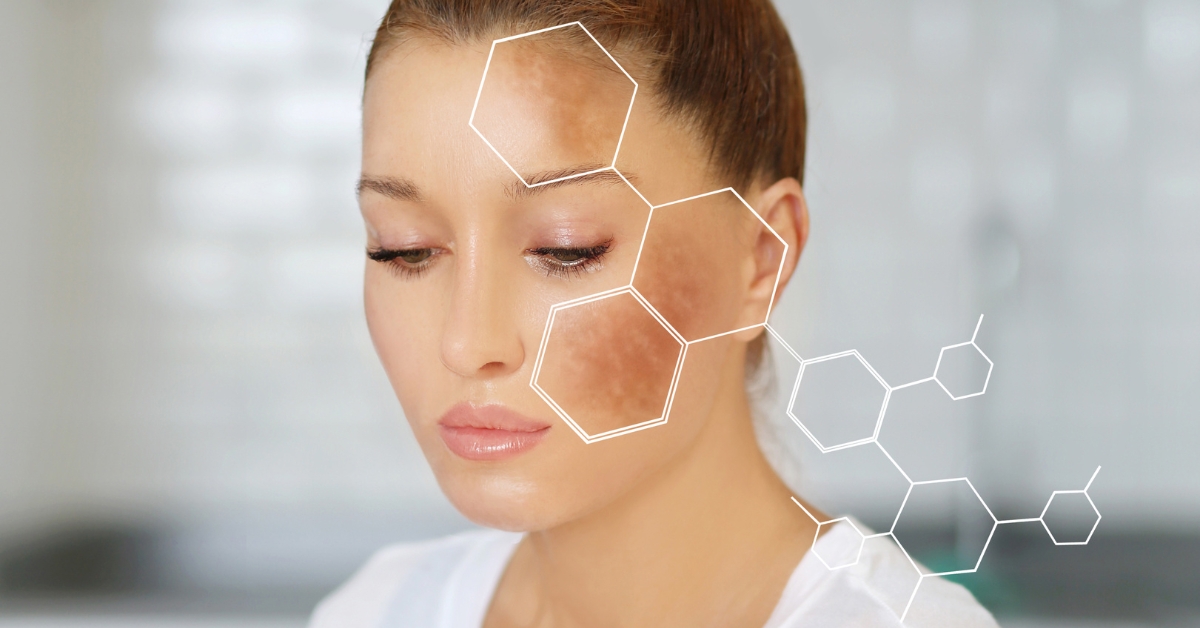
In the field of functional medicine, we understand that skin health is deeply connected to nutrition and the overall well-being of the body. Melanin production, the natural pigment responsible for protecting the skin from ultraviolet (UV) rays and giving it color, is a complex process influenced by nutritional and environmental factors.
Addressing you, health professionals, we want to explore how nutrition can play a key role in promoting healthy skin, particularly in terms of enhancing melanin production naturally. As experts in functional medicine, our goal is to provide a comprehensive, evidence-based perspective that can be applied in your daily practices to improve the quality of life for your patients.
The Importance of Melanin in Skin Health
Melanin not only determines the color of the skin, hair, and eyes, but it also acts as a natural barrier against the harmful effects of UV radiation. In the skin, it is produced by melanocytes, specialized cells that respond to sun exposure by increasing melanin levels to protect the DNA of skin cells from damage that can lead to mutations or skin cancer.
A deficiency in melanin, whether due to genetic or nutritional factors, can result in increased susceptibility to sunburn, oxidative damage, and premature aging of the skin. For patients with fairer skin, this risk is greater, making the promotion of melanin production a crucial aspect of their dermatological health.
Foods That Promote Melanin Production
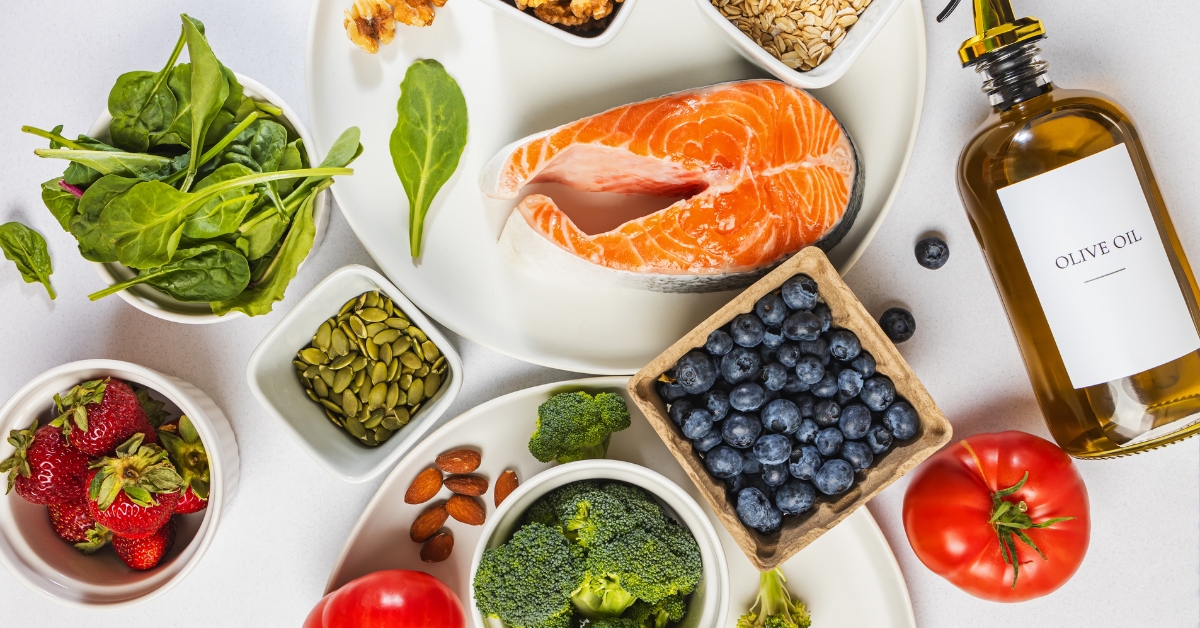
From a functional medicine perspective, we know that nutrition plays a crucial role in all body systems, including the skin. To enhance melanin production, certain nutrients—particularly those with antioxidant properties and rich in carotenoids—have been identified as essential.
- Foods Rich in CarotenoidsCarotenoids are plant compounds that not only help protect the skin from solar damage but also stimulate melanin production. Among the most well-known are beta-carotene, lutein, and lycopene. These can be found abundantly in:
- Carrots: Rich in beta-carotene, they help prepare the skin for sun exposure, reducing susceptibility to burns.
- Leafy Greens (spinach, kale, Swiss chard): These vegetables are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, which not only protect the skin but also play a crucial role in eye health.
- Red and Green Peppers: They contain high amounts of beta-carotene and other antioxidants that promote cellular health and skin pigmentation.
- Orange and Yellow Fruits (peaches, squash, apricots): These are important sources of vitamin C and carotenoids, essential for collagen production and skin pigmentation.
2. Foods Rich in Antioxidants
Melanin production can also be enhanced through a diet rich in antioxidants. These protect skin cells from oxidative stress, which can inhibit melanocyte function. Foods rich in antioxidants include:
-
- Berries (strawberries, blackberries, blueberries): These contain flavonoids and anthocyanins, which are powerful antioxidants with beneficial effects on skin protection.
- Citrus Fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits): High in vitamin C, they support collagen synthesis and cellular repair, indirectly contributing to skin health.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds are rich sources of vitamin E, which protects the skin against free radicals.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods such as salmon, sardines, flaxseed oil, and walnuts, can reduce skin inflammation, which is often related to cumulative damage from sun exposure. Additionally, omega-3s promote cellular repair and can help optimize melanin production by reducing oxidative stress in the skin.

__
How Nutrition Supports Melanocyte Function
Functional medicine emphasizes a holistic approach to supporting melanocyte function. It’s not just about adequate nutrient intake but also about addressing underlying dysfunctions that could be affecting skin health. Among the factors that can negatively influence melanin production are:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Thyroid hormones and cortisol levels directly affect melanocytes and their ability to produce melanin. Proper stress management and hormonal regulation can be key to improving skin health.
- Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies: In addition to carotenoids, other vitamins like D and minerals such as zinc and copper play a fundamental role in skin pigmentation and cellular function.
- Chronic Inflammation: Systemic inflammation can disrupt melanocyte function. Patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, may benefit from nutritional strategies that reduce inflammation and promote skin health.
Nutritional Strategies Based on Functional Medicine
A personalized approach for each patient is essential. Health professionals should consider the following steps to improve their patients’ skin health from a functional perspective:
- Assess the Patient’s Current Diet: Identify deficiencies in key nutrients that affect melanin production.
- Optimize Antioxidant and Carotenoid Intake: Recommend foods rich in carotenoids, vitamins C and E, and healthy fats like omega-3s.
- Incorporate Supplements When Necessary: In cases of severe deficiency or conditions affecting nutrient absorption, supplements of beta-carotene, zinc, or vitamin D may be recommended.
- Adjust Hormonal Imbalances: Working on stress management, improving thyroid function, or adjusting hormonal treatments may be necessary to promote skin health.
- Promote Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Using adequate sun protection, avoiding excessive UV exposure, and ensuring proper hydration are essential complementary practices.
As healthcare professionals, we have the opportunity to educate our patients on how a balanced diet can directly impact their skin health, particularly in the production of melanin.
Adopting a functional medicine approach allows us to offer personalized solutions that not only enhance the aesthetics of the skin but also strengthen the body’s ability to defend itself against environmental aggressors like UV rays.
Furthermore, by maintaining an open dialogue with our patients, we can encourage the adoption of a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This not only helps prevent diseases but also promotes digestive health and improves gut microbiota, fostering greater resilience against chronic conditions.
We invite you to participate in our biweekly webinars, which will take place on Thursdays at 5:00 PM (Pacific Time, -07:00 GMT). In these sessions, we will address current health topics and strategies to optimize our patients’ well-being. Interaction in these spaces is vital for sharing knowledge and experiences, and for strengthening the community of healthcare professionals committed to holistic well-being.
Together, we can significantly impact our patients’ lives by guiding them toward informed and healthy decisions that positively contribute to their long-term well-being.
Dr. Kent Nelson
Functional Wellness Network
www.functionalwellnessnetwork.com
__
__