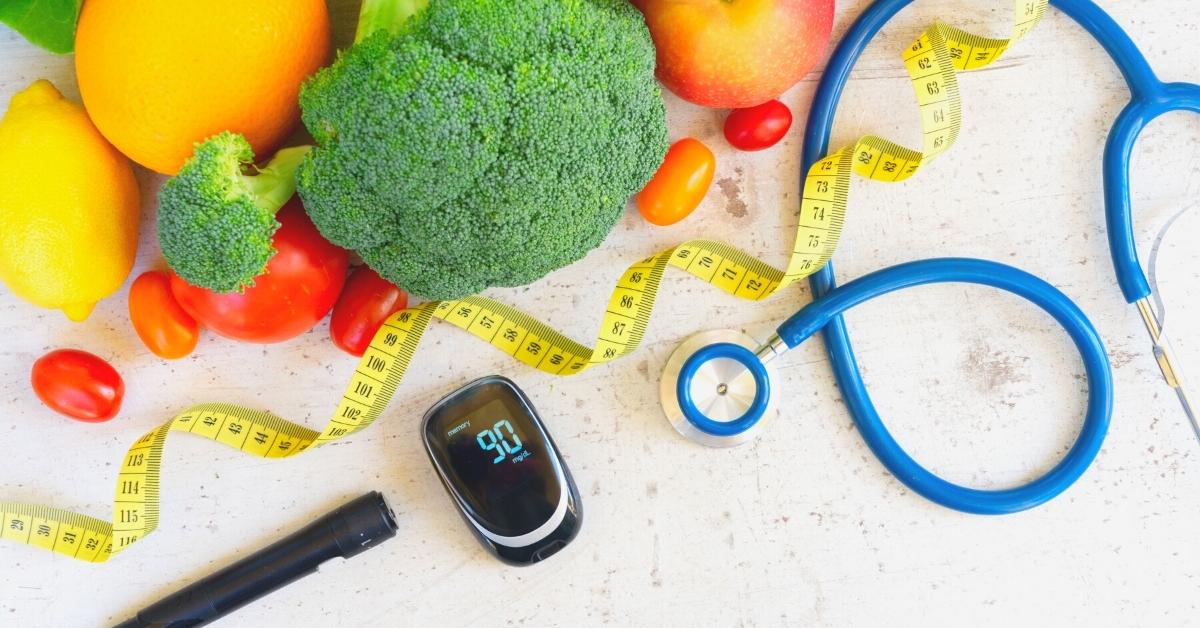
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which the body neither produces enough insulin nor responds normally to it, causing blood glucose (sugar) concentrations to be abnormally high.
Blood sugar
The three main nutrients that make up most foods are carbohydrates, protein and fat. Sugars are one of the three types of carbohydrates, along with starch and fiber.
There are many types of sugars. Some are simple and some are complex. Sucrose (table sugar) is made up of two simpler sugars called glucose and fructose. Lactose (milk sugar) is made up of glucose and a simple sugar called galactose. Starch carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, rice and other similar foods, are long chains made up of different simple sugar molecules. Before sucrose, lactose, carbohydrates and other complex sugars can be absorbed by the body, enzymes in the digestive tract must break them down into simple sugars.
Generally, when simple sugars are absorbed by the body, they are all converted into glucose, which is an important fuel for the body. Glucose is the sugar that travels through the bloodstream and is picked up by the cells. The body can also produce glucose from fats and proteins. It actually means blood glucose.
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas (an organ located behind the stomach that also produces digestive enzymes), regulates the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose in the bloodstream stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin. This insulin helps glucose pass from the blood into the cells. Once inside the cells, it is converted into energy for immediate use or stored as fat or as glycogen or starch until it is needed.
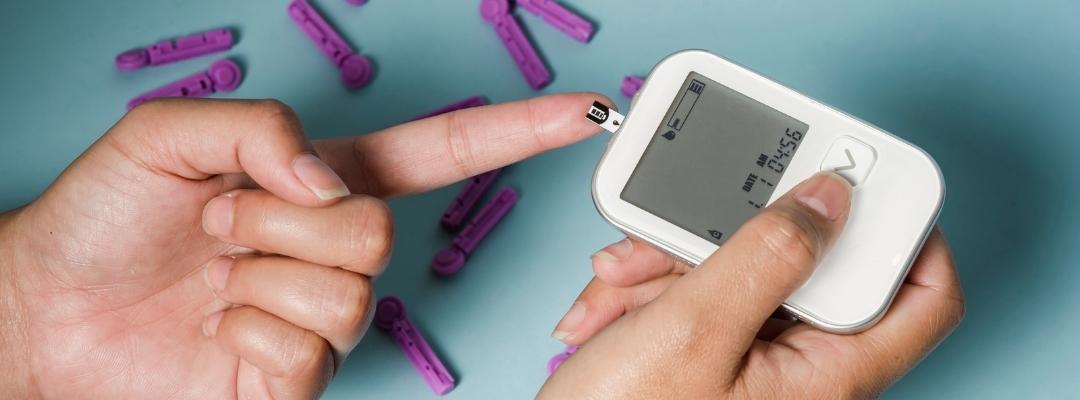
Under normal conditions, blood glucose varies throughout the day, rising after each meal and returning to pre-meal levels over the next 2 hours. When glucose levels return to pre-meal levels, insulin production decreases. The variation in blood glucose is usually within a narrow range, around 70 to 110 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 3.9 to 6.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) of blood under normal conditions. If a large amount of carbohydrates is ingested, blood glucose rises, as it also does after reaching 65 years of age, especially after eating.
Holistic methods to treat diabetes
1. Cinnamon for diabetics
Cinnamon has a compound called methyl-hydroxy-chalcone or MHCP that can improve the cells’ response to insulin. Moreover, it can work together with insulin, which would help to significantly improve blood sugar levels and thus improve diabetes.
2. Berries for fruits
Although berries have been associated with a reduction in glucose levels, the truth is that it is not magic, what happens is that it is a food with a low glycemic index (30) and does not cause drastic fluctuations, so it can be consumed safely.
3. Low glycemic index foods to use for diabetes 4.
- Bulgur
- Quinoa
- High-fiber whole grain cereal, rolled or flaked oatmeal
- Carrots, non-starchy green vegetables
- Apples, oranges, grapes, and many other fruits
- Most nuts, legumes and beans
- Milk and yogurt
4. Daily activity for at least 30-45 minutes
If you have diabetes, physical activity makes your body more sensitive to insulin (the hormone that allows the body’s cells to use blood sugar for energy), which helps manage diabetes. Physical activity also helps control blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of heart disease and nerve damage.
5. Liver cleansing for better glycogen production.
The liver acts as the body’s glucose reservoir, and helps keep circulating blood sugar levels and other body fuels even and constant. The liver stores and also manufactures glucose depending on the body’s need. The need to store or release glucose is primarily signaled by the hormones insulin and glucagon.
Treatment of diabetes mellitus
- Diet
- Exercise
- Weight loss
- Education
- In type 1 diabetes, insulin injections
- In type 2 diabetes, often orally administered drugs and sometimes insulin injections or other drugs
Diet, exercise and education are the cornerstones of diabetes treatment and often the first recommendations given when mild diabetes is diagnosed. In overweight people, it is important to lose weight. People who continue to have high blood glucose levels despite lifestyle changes or whose blood glucose is very high or who have type 1 diabetes (regardless of the blood glucose value) also need to take medication.
Since diabetes complications are less likely to occur if blood glucose is tightly controlled, the goal of treatment is to keep blood glucose values as close as possible to the normal range.

Diabetes mellitus is a serious disease that can lead to many health complications if not properly treated. However, with the right knowledge and tools, you can manage your diabetes and live a long, healthy life. We hope this article has given you some valuable information about diabetes and its treatment. If you have any questions or would like more information, please attend our Zoom meetings every Thursday at 10:00 am. Thank you for reading!
Dr. Mansi Shah
Functional Wellness Network
www.functionalwellnessnetwork.com